1. Reproductive System: Male and Female
Mating, reproduction and propagation are the three umbrella terms which cover the entire bloom of life process. At the time of puberty, several changes are noticed in human males and females regarding their appearances and emotions because nature has its own laws to bring maturity in young boys and girls between the ages range 10-16 years. Around this time, the sex cells divide and subdivide during a process called meiosis. During meiosis, the mature sex cells carrying 46 chromosomes each undergo a twin-division in such a way that the resultant four daughter cells carry 23 chromosomes each. The process is called spermatogenesis in males and oogenesis in females.
Male Puberty and The Male Reproductive system:
The sexual organs of a normal male comprise of the following:
1) Testes (Singular ‘testis’)
2) Seminal Vesicle
3) Prostate Gland
4) Penis

Spermatogenesis takes place in young males in the age group ranging between 12 to 16 years when pituitary gland (near the brain) releases certain hormones that signal the production of testosterone (male sex hormone) in the testes. Under the influence of testosterone, these teenage boys experience internal as well as visible physical changes. Secretion of testosterone brings about chemical changes in the body during which energy and heat are released. Heightened level of energy introduces certain physical changes in teenage males:
1) Growth of facial hair
2) Growth of hair in pubic area, on the chest and in under-arms
3) Voice breaks down and becomes heavier
4) Body becomes muscular
5) Shoulders become square and contribute to the muscular physical build-up
6) Increase in height
7) Pelvic area remains somewhat slim and legs become taller
Internal changes are equally crucial and are responsible for a successful sex life in future. The male body has two testes (right & left). Before puberty, the testes are a tiny network of tubules carrying immature male sex cells. Initially these testes are contracted into the male body and tucked into the abdominal cavity just behind the penis. When testes get the signal to produce testosterone, the immature sex cells stored in both the testes become active and start the twin-division process. After every active sex cell undergoes meiosis, millions of daughter cells are produced.
These male ‘daughter sex cells are called ‘sperms. As the number of cells increase drastically, the contracted testes descend into the ‘scrotum’ an external loosely hanging skin bag which is located just behind the penis. The sperms produced by the testes are stored in a tissue structure, ‘epididymus’, closely attached to the testes. Epididymus is a sperm depository which releases sperms every now and then. Sperm duct (Vas Deferens) is a tiny tube attached to the posterior of the epididymus, runs vertically into the pelvis and goes all the way round the right side of the bladder and coming back through the left side is connected to seminal vesicle and prostate gland, ending into the urethra which is a common medium for urination and sperms’ ejaculation in males. Seminal vesicle releases a viscous, off-white creamy material to provide better lubrication thus enhancing the smooth flow of sperms; prostate gland releases chemicals for better motility of the sperms. Both seminal vesicle and the prostate gland give out their secretions whenever sperms are released from the epididymus through the sperm duct. sperms may be released whenever a mature engages in a real sexual act, fantasises about sex, engages in self-indulgence (masturbates) or simply passes out urine.
Millions of sperms pass out of the body through the penis during any of these activities. The penis is made up of tough tissues which can contract when the penis is not in any vital use (such as urination or having sex) and can expand, stiffen and elongate when a male passes out urine or is sexually active. In the latter case, the penile tissues are richly supplied with blood and thus the penis gains erection. During sex the penis has to be erect and tough to be able to thrust its way into the female vaginal track.
Female Puberty and The Female Reproductive System:
In females, the reproductive organs are all located inside the pelvic area. In this respect the females are different from males as no organ contributing to the sexual realm is seen outside the body except the genitalia that is a common source for excreting urine, menstrual blood and receiving male’s penis during sexual intercourse. An infant girl is born with huge numbers of microscopic eggs already present in her ovaries. These eggs remain dormant (inactive) until the girl attains puberty (10-14 years old). At the time of puberty the pituitary gland sends signals all over the female’s body to prepare itself for internal and external changes. Visible changes in physical appearance are: breasts spurt, growth of hair on pubic area and in underarms, widening of hips, body becomes fleshier; wrists, shanks and thighs become rounder and more fats accumulate around waist and thighs which make the female body look heavier. The female body gains girth (thickness) around pelvis because this is where the new life emerges from in future. The pelvis area makes up the reproductive system of the female. The reproductive system of a human female consists of the following organs:
1) Ovaries (Right and Left)
2) Fallopian Tubes (Right and Left)
3) Uterus
4) Cervix
5) Vagina

Internal changes start simultaneously at the same time when the external changes take place. Internally, the female hormone, oestrogen is released by the right and the left ovaries due to the signals received by the pituitary gland. Oestrogen drives the inactive eggs in the ovaries to maturity and then each egg undergoes meiosis which in females is also known as oogenesis. In this process, each mature sex cell, carrying 46 chromosomes divides twice and the four daughter cells are released each carrying 23 chromosomes. The process is slow enough to give a girl time to grow into a mature female. In the last stage of puberty, both ovaries are full of mature eggs.
The entire reproductive system of a female, if viewed from distance, looks like an inverted pear (uterus) with outstretched arms (fallopian tubes) embracing two egg-shaped muscular balls (ovaries). During meiosis eggs are matured, divided and subdivided in both the ovaries. In a mature female, each ovary releases an egg alternatively, once a month. In this way, only one ovary is set to work in one month while the other ovary waits for its turn in the next month. Each ovary is attached to the fallopian tube through hundreds of finger-like structures called fimbriae which catch the egg upon its release from the ovary. Both fallopian tubes are lined with hair-like projections growing inwards called cilia which provide smooth movement to the egg through the fallopian tube into the uterus. While the egg is still in the fallopian tube, if it comes across a sperm, discharged by a male during sex, and if the egg is successfully fertilized by the sperm, the zygote (male sperm + female egg) descends into the uterus and gets implanted in the inner wall of the uterus (womb). In case a female has no sex, the egg simply descends into the uterus and is expelled through the vagina during menstruation. Menstruation is the blood that flows out of the uterus which sheds the tissue lining of its own walls to refresh itself and prepare to release the next egg.
Sexual Reproduction in Human Beings:
When human beings want to reproduce, both male and female partners have to participate actively in this act. This act, usually known as sexual intercourse, sometimes involves a great deal of foreplay to bring both partners to a proper arousal. Foreplay involves a set of emotional overflow and physical stimulation. Both the partners experience an increase in blood pressure, heart beat and breathing. Blood rushes towards the brain and the genitals and as a result the body temperature starts rising. While blood rush and willingness for sex causes erection in male’s penis, the female develops stiffness on her breasts’ nipples and flexibility in her vaginal muscles. The female also experiences some vaginal discharge which moisturizes the vagina to encourage a smooth entry of the penis. The male inserts his penis into the female’s vagina. While the penis increases its girth with the passing moments, contractions develop in the testes and millions of sperms are released. These sperms, travelling through Vas Deferens, are richly lubricated by a viscous slimy off-white cream textured material released by ‘seminal vesicle’ and ‘prostate gland’. All together the composition is called semen which is ejaculated into the vagina with force in a series of pelvic thrusts by the male partner. As the contractions of the testes subside, the male relaxes and loses his urge. A complete sexual act leaves millions of sperms in the female vagina from where the sperms swim through the cervix into the uterus (womb). The possibility of pregnancy is the highest from day 16th – day 20th after the first day from the menstrual cycle. Around this time either ovary has released a fresh egg which would be travelling through the fallopian tube. In around 48 hours, the sperms ascend the uterine cavity and spread into both the fallopian tubes.
The fallopian tube carrying the egg is more important at this time as there is possibility of fertilization here. Thousands of sperms compete towards the egg but only one sperm is able to penetrate it. The fusion of the female egg (23 chromosomes) and the sperm (23 chromosomes) results in a zygote (23 +23=46 chromosomes). Zygote is a multicellular blastocyst (cellular ball full of fluid). The blastocyst descends into the uterus and attaches itself to the uterine wall (to get nourishment and also to avoid getting ping-ponged against the uterine walls). This process is called implantation. The female hormones oestrogen and progesterone maintain the endometrial thickness, facilitate blood supply and nutrients to the zygote. The blastocyst is divided into an inner cellular body and an outer membrane. The inner cells propagate to shape baby’s body and the outer membrane thickens to form placenta (a spongy cover around the baby for protection)In 2-3 months the zygote grows into an ‘embryo’ (brain, heart, stomach, intestines and muscles are formed in miniature), after this stage the embryo’s body parts become clearly visible and it is called a ‘foetus’. The placenta is attached to the uterus through a thin muscular tube called ‘umbilical cord’. This cord is a medium through which the baby gets its nutrients and oxygen in the womb. If the pregnancy is free from complications, the baby increases its size and during the last two weeks of the ninth month takes its position (upside down) at the cervix. The hormones released this time cause contractions in the uterus and also aid the cervix to dilate (loosen and open itself). The contractions push the baby through the dilated cervix out of the body.
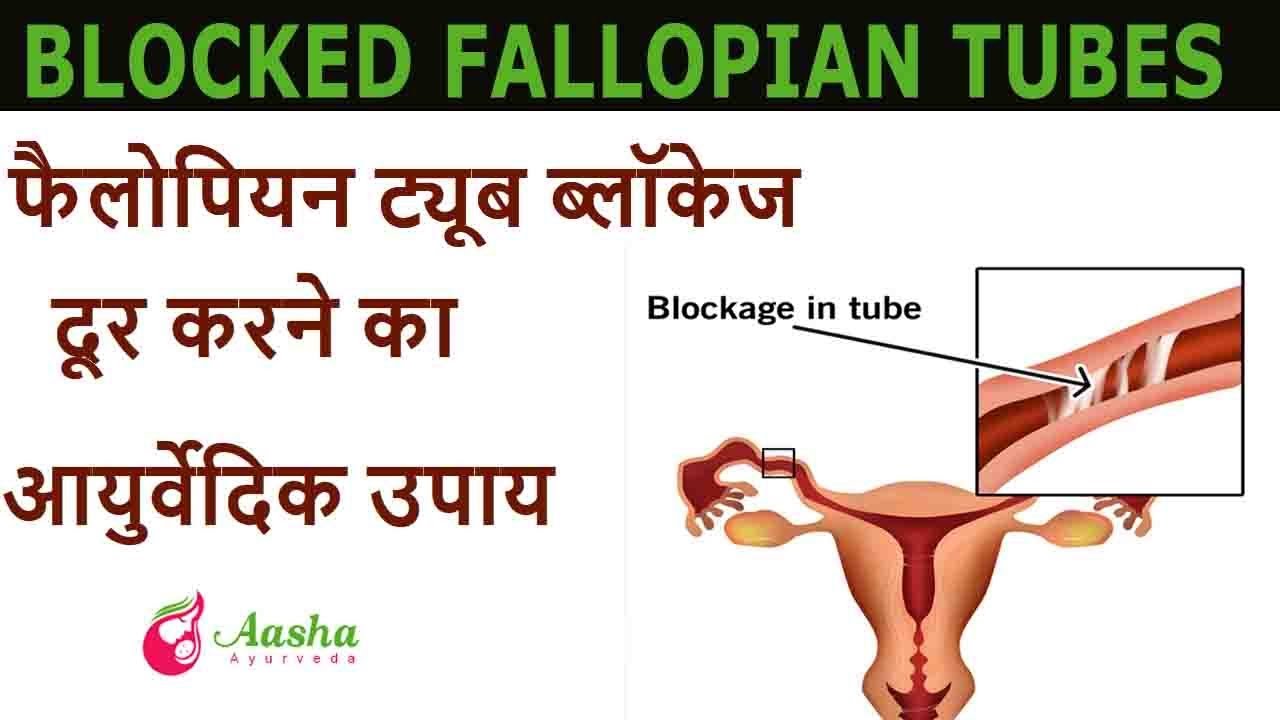
Causes for Blocked Fallopian Tubes:
Some couples have difficulty in producing children because of infertility issues. These issues can be temporary diseases, blockages in vital reproductive parts, inflammation or heredity factors. Sometimes a female fails to conceive even after having a normal menstrual cycle. There is a possibility of blockage in her fallopian tubes. This condition has two primary causes:

1) Inflammation in a particular region of the fallopian tube; the part nearest to the ovaries is the most likely to be affected.
2) Outgrowth of the uterine tissues which may partially start climbing into the fallopian tube and block the passage, a situation that does not allow great number of sperms to swim easily into the fallopian tube.
Both the ‘inflammation’ and the ‘outgrowth’ indicate towards the possibility of the creation of a ‘scar tissue’ or ‘hard tissue’ in the fallopian tube that hinders the free flow of sperms towards inside. Females willing to conceive have to be alert in case they come across any of the following symptoms:
1) If they fail to conceive within one year even after leading a healthy sexual life.
2) Pain in the pelvic area or abdominal spasms with weak frequency or more frequently.
3) Female may have ‘ectopic pregnancy’ as the zygote (fertilized egg) is not able to descend into the uterine area for implantation due to blocked passage. In this case contact your doctor as soon as possible.
The symptoms listed above do prove to be very serious if neglected. If you seek medical aid, the doctor will guide you to go for a series of tests without wasting any time. An ultra sound test, ink X-Ray or Laparoscopy are considered somewhat effective to detect the reason of the disorder. In colour X-Ray, some harmless quality of ink is inserted into the uterus through an injection. The passage of the ink is tested whether it is able to flow freely into the fallopian tubes or not. The here symbolises the sperms. In Laparoscopy, a tiny camera is descended into the uterus through a hole in the patient’s body. This camera facilitates in getting a ‘live’ image of the internal uterine area and helps the doctor in detecting the reason for the blockage.
Home Remedies To Treat Blocked Fallopian Tubes
If your doctor confirms blocked fallopian tubes in you, don’t take as a doom or the end of the world for you. It is true that you can resort to medical treatment in a well known fertility clinic or hospital but that is not without side effects. It is better not to indulge in an obsession of taking medicinal drugs. Such a female patient should rather give a second thought to her life style and her food habits so that she can modify them positively. Critically analyse your needs and indulges and select the ones that need a work out and eliminate the that harm you.
Top 10 Home Remedies:
1) Increase the intake of Vitamin C and make it an inseparable part of your daily diet. You need not entirely depend on it but your mail meals should be followed by a generous serving of citrus fruits like oranges, kiwi and grapefruits. Some drops of lemon sprinkled over your meal or a glass of lemonade once a day is highly appreciable. As Vitamin C is known for absorbing the infection and drying the wounds of their perpetual moisture and inflammation, it will help to relieve the inflammatory portion of the fallopian tubes.
2) Some spices are known for boosting motherhood qualities in a female human body a situation that would lead to conceive a child. Food attributes like turmeric and cumin seeds are highly effective when fried in pure ghee and added to the meals.
3)Ginger and cinnamon are well-known anti-inflammatory agents and can do wonderful job in checking overgrowing tissues in the uterus. They can also contribute to better blood flow in male reproductive organs thus enhancing sperm motility in a male body,. Garlic intake can be encouraged through frying it in olive oil and sprinkling it over your dish.
4) Avoid junk foods or those that can cause hormonal imbalance. Keep a check on showy and taste buds ticklers like spicy burgers, pizzas, road-side oily purees and processed mix spices. Prefer to rely on home ground spices (masala), coconut oil and olive oil for cooking.
5) Ginger tea and coffee help to start an anti-oxidant day but they have been consumed in the limit. One cup morning ginger tea and one cup evening coffee are appreciable.
6) Foods that can regulate growing tissues in the body are eggs. They provide warmth to the body and contribute a lot to the reproductive organs as they themselves are produced for the reproductive purpose in the family poultry.
7) Some specific fruits and vegetables are capable of detoxifying the reproductive organs. Try to keep a list ready with you according to the season as to which fruit should be your priority. Red and yellow fruits are known for richer vitamins, such as red apples, mangoes, figs and papaya.
8) Prepare rich salad comprising carrot, radish and bell peppers. Bell peppers are best sources of vitamins if eaten raw in a salad form with sprinkled lemon drops.
9) Make yourself stress free. Try not taking it to your heart that you have a problem in conceiving. Be positive and derive pleasure from natural gifts. Sometimes reading is also effective as it induces good sleep. If you are a habitual smoker or liquor consumer, quit them at once. Develop a habit of waking up early in the morning and practice meditation for at least fifteen minutes. Try to sit with crossed-legs, remain calm and give importance to your existence.
10) Yoga Asanas that may stretch and increase activity in pelvic muscles. ‘Bridge Pose’ is famous in this regard and if you are slim bodied female you can do it easily. Lying on your back with knees into your abdominal area, try to raise your pelvis a bit high and inhale. Release the pelvis and exhale after 2-3 seconds.
‘Viparita Karani’ is easier for ladies of heavy build-up. Lie on your back beside a wall with your hips resting against the wall and relax for a few moments. Use a mat for lying to avoid hurting your back. Raise your legs high in the air so that your legs make a right angle (90 degree) against your rest of the body. The technique is helpful by providing most blood flow to the fallopian tubes. Keep in this posture for 10-15 minutes then lie down straight and relax.
Blocked Fallopian Tubes Treatment in Ayurveda
Ayurvedic infertility treatment can contribute herbal potions which are famous for treating visible and invisible signs of some diseases such as blocked fallopian tubes. Take the dosage of herbal medicines calmly because the success rate of Ayurvedic medicine increases manifolds with the discipline of its consumption.
Ayurvedic physicians can guide you how to massage with Castor oil and Olive oil, both having warmth giving quality in them. Both of them relieve muscles and boost blood circulation. Luke warm castor and olive oils’ massage, once a day, over the pelvic area helps in the removal of fallopian blockage, elimination of old and dead cells through better menstruation, providing warmth to the body and strength to combat the muscular diseases. For effective results, use one type of oil at a time and avoid mixing both the oils in one vessel.
Ayurvedic Medicine to Unblock Fallopian Tubes
Herbal Pills can also be used for fallopian treatment as these pills are prepared from herbal extracts. Fuyan pill is prepared from the herbs used by therapists who follow traditional Chinese methods to cure patients of sensitive diseases. Actually Ayurvedic medicine has always shown an upper hand when it comes to fertility treatment. A doctor who is expert in herbal medicines can decide your dosage of remedies such as Dong Quai and Red Peony Root. These medicines are also available as substitutions in the market, so don’t try to consume them without a prescription from a well known practitioner. Ayurvedic treatment is also positively effective in females with PCOS as it boosts the maturity process of eggs by activating specific hormones. The entire medicinal course has to be observed for 4-6 months and after that a second visit to the doctor will tell you about the nature of the progress.
Remember to consult your doctor for each step that you follow at home and intimate your doctor regarding the changes that appear on you from time to time. In a hub of hospitals and clinics like the city of Delhi, you may rely on several doctors. Keep in mind the level of hygiene and staff dealings before everything. Rajouri Gardens is an area that should be your first choice for a gynaecologist, Dr. Chanchal Sharma (Asha Fertility) and her handpicked staff of friendly fellows who deal with the patients more like friends. Moreover her healing techniques have invited a lot more baby chuckles in happy homes. So no more depression about your hopeless life and prepare to start a new journey towards Hopeful (Asha) motherhood.



